

The customers have a lot of power when there aren’t many of them and when the customers have many alternatives to buy from. The bargaining power of buyers is also described as the market of outputs. This force analyzes to what extent the customers are able to put the company under pressure, which also affects the customer’s sensitivity to price changes. Boeing and Airbus therefore have substantial bargaining power on the prices they charge. In terms of aircrafts for example, only two major suppliers exist: Boeing and Airbus. The price of aviation fuel is subject to the fluctuations in the global market for oil, which can change wildly because of geopolitical and other factors.

These inputs however are very much affected by the external environment over which the airline companies themselves have little control. The bargaining power of suppliers in the airline industry can be considered very high. When looking at the major inputs that airline companies need, we see that they are especially dependent on fuel and aircrafts. Sources of supplier power also include the switching costs of companies in the industry, the presence of available substitutes, the strength of their distribution channels and the uniqueness or level of differentiation in the product or service the supplier is delivering. Businesses are in a better position when there are a multitude of suppliers. The fewer there are, the more power they have. The concentration of suppliers and the availability of substitute suppliers are important factors in determining supplier power. This force analyzes how much power and control a company’s supplier (also known as the market of inputs) has over the potential to raise its prices or to reduce the quality of purchased goods or services, which in turn would lower an industry’s profitability potential.

Porter’s Five Forces Video Tutorial Bargaining power of suppliers Many low-cost carriers like Southwest Airlines, RyanAir and EasyJet have successfully entered the industry over the years by introducing innovative cost-cutting business models, thereby shaking up original players like American Airlines, Delta Air Lines and KLM. Even though it doesn’t sound very attractive for companies to enter the airline industry, it is NOT impossible. However, due to the liberalization of market access and the availability of leasing options and external finance from banks, investors, and aircraft manufacturers, new doors are opening for potential entrants. A new entrant is likely to not have this kind of expertise, therefore creating a competitive disadvantage right from the start. Furthermore, it can be expected that existing players have built up a large base of experience over the years to cut costs and increase service levels. Moreover, new entrants need licenses, insurances, distribution channels and other qualifications that are not easy to obtain when you are new to the industry (e.g. It takes quite some upfront investments to start an airline company (e.g. The threat of new entrants in the airline industry can be considered as low to medium.
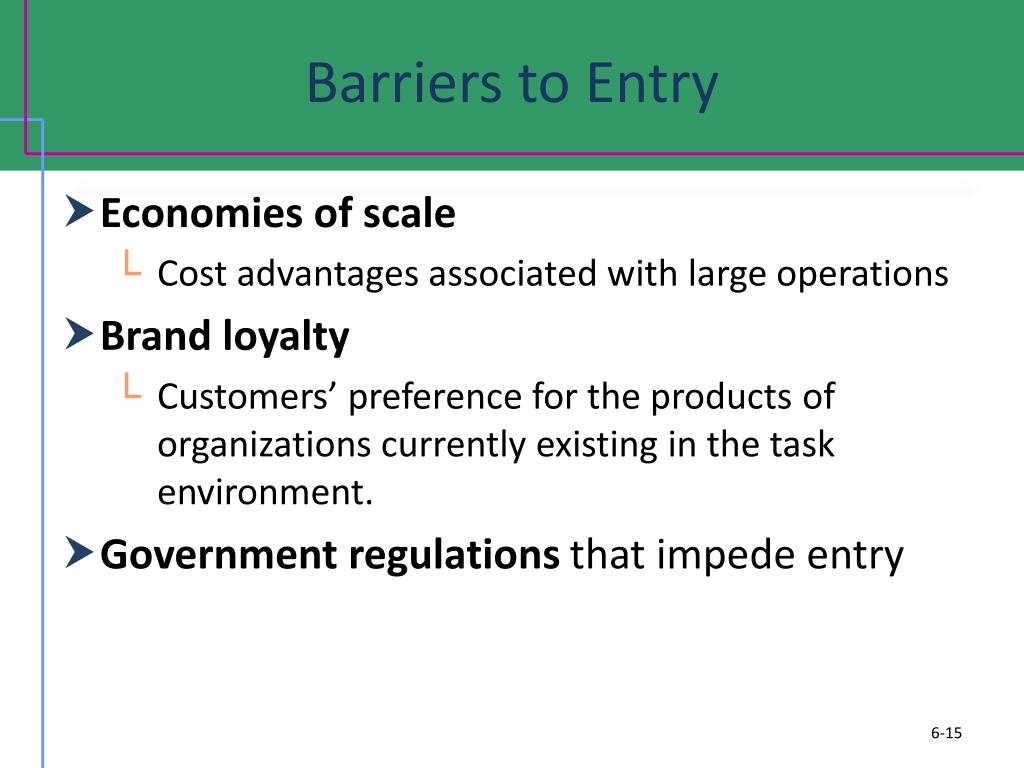
More barriers can be found in the table below. large investments in marketing or R&D), the need for cumulative experience, government policies, and limited access to distribution channels. Examples of barriers to entry are the need for economies of scale, high customer loyalty for existing brands, large capital requirements (e.g. The higher these barriers to entry, the smaller the threat for existing players. The seriousness of the threat depends on the barriers to enter a certain industry. New entrants in an industry bring new capacity and the desire to gain market share. Each force will be elaborated on below with the aid of examples from the airline industry to illustrate the usage.įigure 1: Five Forces Model Threat of new entrants softdrink industry), there is room for higher returns. airline industry), almost no company in the industry earns attractive returns on investments. The collective strength of these forces determines the profit potential of an industry and thus its attractiveness. Rather, the state of competition in an industry depends on five basic forces: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products or services, and existing industry rivalry. According to this framework, competitiveness does not only come from competitors. It is especially useful when starting a new business or when entering a new industry sector. Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a framework that helps analyzing the level of competition within a certain industry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
